In forex, everything is relative. That is no less the case for forex volatility, which is low relative to the spikes in 2008 (credit crisis) and 2010 (EU Sovereign debt crisis), but high relative to the preceding 5+ years of stability. On the one hand, volatility is approaching a two year low. On the other hand, analysts continue to warn of high volatility for the foreseeable future. Under these conditions, what are (currency) investors supposed to do?!
Despite the steady pickup in risk appetite in 2010, there remains a whole a host of forex risk factors. On the economic front, GDP growth remains anemic in western countries, unemployment is high, and consumer confidence is low. Budget deficits and national debts are rising, perhaps to the point that default by a major industrialized countries is inevitable. Emerging market countries seem to be ‘suffering’ from the opposite problem, whereby rapid growth, high commodities prices, and capital inflow has caused inflation to rise precipitously. Some Central Banks will be forced to hike interest rates, while others will try to maintain an easy monetary policy for as long as possible. Political crises flare-up without warning, the Euro risks breaking up, and inclement weather is wreaking havoc on food production.
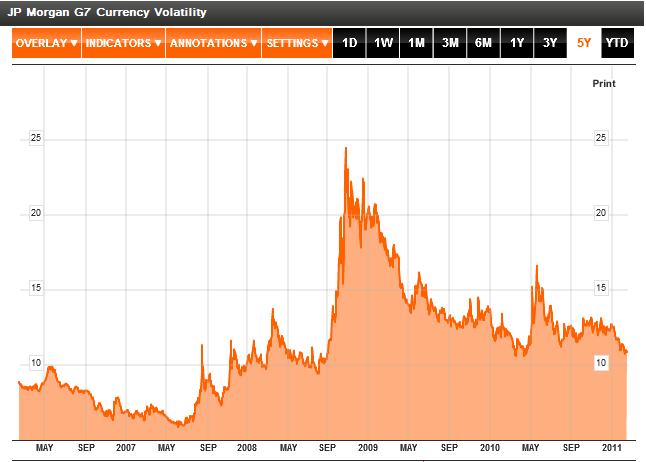 As a result, most currency-market watchers expect 2011 to be a continuation of 2010. In other words, while we might be spared a major crisis, a generalized sense of uncertainty will continue to pervade forex. According to JP Morgan, “Implied volatility on options for major exchange rates averaged 12.34 percent this year, compared with an average of 10.6 percent since January 2000.” The currency team of UBS predicts, “The divergence between the strength in emerging markets and the unusual levels of uncertainty in the world’s major economies will cause…super volatility,” whereby massive swings in exchange rates will become the norm.
As a result, most currency-market watchers expect 2011 to be a continuation of 2010. In other words, while we might be spared a major crisis, a generalized sense of uncertainty will continue to pervade forex. According to JP Morgan, “Implied volatility on options for major exchange rates averaged 12.34 percent this year, compared with an average of 10.6 percent since January 2000.” The currency team of UBS predicts, “The divergence between the strength in emerging markets and the unusual levels of uncertainty in the world’s major economies will cause…super volatility,” whereby massive swings in exchange rates will become the norm.
In this environment, there are a number of things that currency traders should do. The first step is simply to be aware that volatility remains high, which means that wider-than-average fluctuations shouldn’t be a surprise. The next step is to decide whether you think that this volatility will remain at an elevated level for the near-term, or whether you expect it to continue declining. (It’s worth pointing out that volatility is not necessarily a perception of absolute risk, but investor perception of risk). The final step is deciding if/how you will tailor your trading strategy in response to changes in volatility.
In fact, you don’t necessarily need to limit your exposure to volatility. If you are a fundamental investor with a long-term approach, you may very well choose to write-off short-term fluctuations as noise. (Of course, if you are a short-term swing trader, you can’t afford to be quite so indifferent). In addition, if your primary interest is in another asset type, you may choose not to hedge any currency risk. Perhaps you believe that the base currency will continue appreciated and/or you relish the exposure to currency movements as an added benefit of asset price exposure. Along these lines, “During the planning stages of the UBS Emerging Markets Equity Income fund, UBS Global Asset Management considered offering investors a hedged share class. The team abandoned the idea when investors showed a preference for unhedged share classes.”
In addition, hedging currency risk is expensive, especially for exotic/illiquid currencies, and currencies characterized by above average volatility. Not to mention that currency hedges can still move against investors, resulting in heavy losses. Still, in 2010, “Corporations from the U.S., Japan and Europe increased the percentage of projected income protected against swings in exchange rates to a record,” which suggests that fear of adverse exchange rate movements still predominates.
Finally, there are those that want to construct second-order currency strategies based entirely on volatility. Using basic options techniques, such as spreads and straddles, it’s possible to profit from volatility (or lack thereof) regardless of which direction the underlying currencies move in. In fact, the CME Group recently introduced a new product series which seeks to perform this very function. Investors can already buy and sell futures based on short-term volatility in the EUR/USD, which will soon be replicated for all of the major currency pairs.
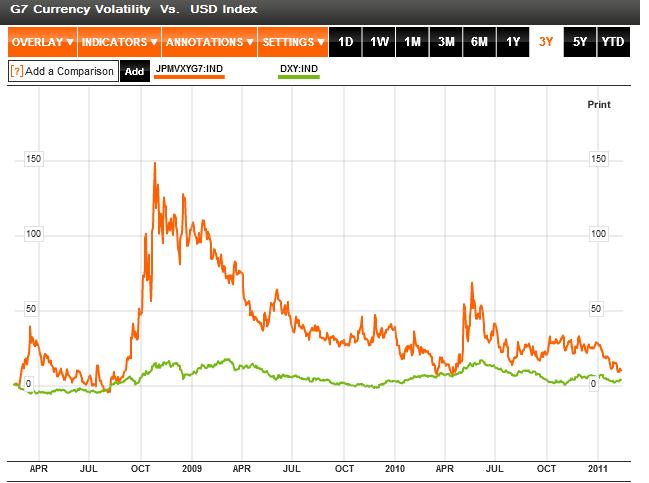
For those of you who like to keep it simple, it’s probably enough to monitor the JP Morgan G7 Currency Volatility Index, which is a good proxy for the risk associated with trading (major) currencies at any given time. When this index spikes, chances are the US Dollar and other safe haven currencies will follow suit.
Despite the steady pickup in risk appetite in 2010, there remains a whole a host of forex risk factors. On the economic front, GDP growth remains anemic in western countries, unemployment is high, and consumer confidence is low. Budget deficits and national debts are rising, perhaps to the point that default by a major industrialized countries is inevitable. Emerging market countries seem to be ‘suffering’ from the opposite problem, whereby rapid growth, high commodities prices, and capital inflow has caused inflation to rise precipitously. Some Central Banks will be forced to hike interest rates, while others will try to maintain an easy monetary policy for as long as possible. Political crises flare-up without warning, the Euro risks breaking up, and inclement weather is wreaking havoc on food production.

In this environment, there are a number of things that currency traders should do. The first step is simply to be aware that volatility remains high, which means that wider-than-average fluctuations shouldn’t be a surprise. The next step is to decide whether you think that this volatility will remain at an elevated level for the near-term, or whether you expect it to continue declining. (It’s worth pointing out that volatility is not necessarily a perception of absolute risk, but investor perception of risk). The final step is deciding if/how you will tailor your trading strategy in response to changes in volatility.
In fact, you don’t necessarily need to limit your exposure to volatility. If you are a fundamental investor with a long-term approach, you may very well choose to write-off short-term fluctuations as noise. (Of course, if you are a short-term swing trader, you can’t afford to be quite so indifferent). In addition, if your primary interest is in another asset type, you may choose not to hedge any currency risk. Perhaps you believe that the base currency will continue appreciated and/or you relish the exposure to currency movements as an added benefit of asset price exposure. Along these lines, “During the planning stages of the UBS Emerging Markets Equity Income fund, UBS Global Asset Management considered offering investors a hedged share class. The team abandoned the idea when investors showed a preference for unhedged share classes.”
In addition, hedging currency risk is expensive, especially for exotic/illiquid currencies, and currencies characterized by above average volatility. Not to mention that currency hedges can still move against investors, resulting in heavy losses. Still, in 2010, “Corporations from the U.S., Japan and Europe increased the percentage of projected income protected against swings in exchange rates to a record,” which suggests that fear of adverse exchange rate movements still predominates.
Finally, there are those that want to construct second-order currency strategies based entirely on volatility. Using basic options techniques, such as spreads and straddles, it’s possible to profit from volatility (or lack thereof) regardless of which direction the underlying currencies move in. In fact, the CME Group recently introduced a new product series which seeks to perform this very function. Investors can already buy and sell futures based on short-term volatility in the EUR/USD, which will soon be replicated for all of the major currency pairs.

For those of you who like to keep it simple, it’s probably enough to monitor the JP Morgan G7 Currency Volatility Index, which is a good proxy for the risk associated with trading (major) currencies at any given time. When this index spikes, chances are the US Dollar and other safe haven currencies will follow suit.
ليست هناك تعليقات:
إرسال تعليق